An abdominal scan, also known as an abdominal ultrasound, is a non-invasive imaging procedure that uses high-frequency sound waves to create real-time images of the organs and structures within the abdomen. It helps assess the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, and bladder, providing valuable information about their size, shape, texture, and any abnormalities. The difference between pelvic scan and abdominal scan is that the abdominal scan focuses on the organs within the abdominal cavity, while the pelvic scan examines the reproductive organs and surrounding tissues in the pelvic area.
| Scan Type | Purpose | Organs Assessed | Conditions Detected | Technique |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abdominal Scan | To assess organs inside the abdominal cavity and evaluate their size, shape, texture, and abnormalities. | Liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, bladder; also major abdominal blood vessels. | Liver disease, gallstones, pancreatic abnormalities, kidney stones, abdominal tumours. | Non-invasive ultrasound using high-frequency sound waves; transducer moved across abdomen to produce real-time images. |
| Pelvic Scan | To examine reproductive organs and surrounding pelvic structures. | Females: uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes. Males: prostate gland. Both: bladder and surrounding tissues. | Females: fibroids, ovarian cysts, PCOS, endometriosis, PID, pregnancy monitoring. Males: prostate enlargement or tumours. | Non-invasive ultrasound using sound waves and a transducer to create real-time pelvic images. |
| Overlap Between Both | Both can assess shared structures when needed. | Bladder and adjacent tissues. | Bladder stones, tumours, abnormalities. | May be combined as transabdominal + transvaginal (for females) for full evaluation. |
Abdominal Scan
The primary goal of an abdominal scan is to assess the organs located in the abdominal cavity, which include the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, and bladder, among others. It gives useful information regarding the size, shape, texture, and anomalies of various organs. An abdominal scan can aid in the diagnosis of illnesses such as liver disease, gallstones, pancreatic abnormalities, kidney stones, and abdominal tumours. It may also measure blood flow in the main blood arteries of the abdomen.
An abdominal scan, often known as an abdominal ultrasound, is a non-invasive imaging process that obtains precise pictures of the organs and structures within the belly. It employs the utilisation of high-frequency sound waves to generate real-time visuals on a display. During an abdominal scan, a portable instrument called a transducer is softly dragged across the skin of the belly, producing sound waves and recording the returning echoes to produce pictures.
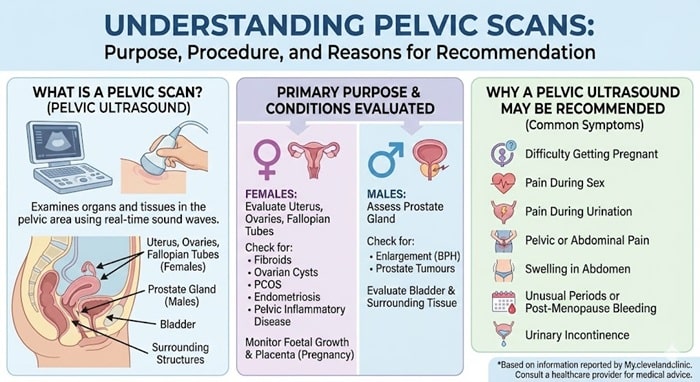
Pelvic Scan
A pelvic scan, often known as a pelvic ultrasound, examines the organs and tissues in the pelvic area. The pelvic region comprises the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes (in females), prostate gland (in men), bladder, and surrounding structures. A pelvic scan, like an abdominal scan, creates real-time pictures using sound waves and a transducer.
The primary goal of a pelvic scan is to check the reproductive organs in both males and females. It aids in the evaluation of the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes in females for disorders such as fibroids, ovarian cysts, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, and pelvic inflammatory disease. It is also used during pregnancy to monitor foetal growth and assess the placenta. A pelvic scan in men can assist check the prostate gland for diseases such as enlargement (benign prostatic hyperplasia) or tumours.
As reported by My.clevelandclinic:
A healthcare provider may recommend a pelvic ultrasound if you have:
- Difficulty getting pregnant.
- Pain during sex.
- Pain during urination.
- Pelvic or abdominal pain.
- Swelling in your abdomen.
- Unusual periods or bleeding after menopause.
- Urinary incontinence (urine leakage).
Differences and overlaps
While the abdominal scan focuses on the organs within the abdominal cavity, the pelvic scan focuses on the reproductive organs and surrounding tissues in the pelvic area. However, there is considerable overlap between the two images. Both scans, for example, can look for bladder anomalies like stones or tumours. In some situations, a healthcare expert may propose a combination of both scans, known as a transabdominal and transvaginal ultrasound, to obtain a full examination of the abdominal and pelvic areas.

Conclusion
Finally, an abdominal scan and a pelvic scan are two independent imaging techniques that give useful information about various parts of the body. The abdominal scan focuses on the organs within the abdominal cavity, whereas the pelvic scan focuses on the reproductive organs and associated tissues in the pelvic area. Both scans are non-invasive, safe, and commonly used to identify a variety of disorders. If you have particular symptoms or concerns about your abdomen or pelvis, it is critical that you contact with a healthcare practitioner who can prescribe the best scan for your unique requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an abdominal scan?
An abdominal scan (abdominal ultrasound) is a non-invasive imaging procedure that uses high-frequency sound waves to create real-time images of organs within the abdomen, such as the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, and bladder.
What information does an abdominal scan provide?
It provides details about the size, shape, texture, and abnormalities of abdominal organs and can help diagnose conditions such as liver disease, gallstones, pancreatic issues, kidney stones, and abdominal tumors.
How is an abdominal scan performed?
A handheld device called a transducer is gently moved across the abdomen, sending sound waves and capturing returning echoes to produce real-time images.
What is a pelvic scan?
A pelvic scan (pelvic ultrasound) examines the organs and tissues in the pelvic area, including the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes (in females), prostate gland (in males), bladder, and surrounding structures.
What conditions can a pelvic scan diagnose in females?
It can evaluate disorders such as fibroids, ovarian cysts, PCOS, endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, and is also used during pregnancy to monitor fetal growth and assess the placenta.
What conditions can a pelvic scan help detect in men?
It can assess the prostate gland for issues such as enlargement (BPH) or tumors.
When might a healthcare provider recommend a pelvic ultrasound?
- Difficulty getting pregnant
- Pain during sex
- Pain during urination
- Pelvic or abdominal pain
- Abdominal swelling
- Unusual periods or bleeding after menopause
- Urinary incontinence (urine leakage)
What is the main difference between an abdominal scan and a pelvic scan?
An abdominal scan focuses on organs within the abdominal cavity, while a pelvic scan evaluates the reproductive organs and pelvic tissues.
Do abdominal and pelvic scans overlap in any areas?
Yes. Both can assess bladder abnormalities, such as stones or tumors.
Great simple explanation! I didn’t realize the abdominal scan covers the spleen and kidneys while the pelvic scan is more focused on reproductive health (uterus/prostate). Very clear difference. Saved this for future reference!
I’m a bit confused and honestly concerned 😕 If someone has ongoing lower abdominal pain, how do doctors decide whether an abdominal scan is enough or if a pelvic scan is also necessary? It sounds like there’s quite a bit of overlap, especially with the bladder. I worry that people might assume one scan covers everything when it actually doesn’t Should patients ask specifically for both if symptoms aren’t clear?
I found this breakdown super helpful. I’d never really thought about the difference between an abdominal and pelvic scan before. It’s interesting that abdominal scans focus on organs like the liver, kidneys, and pancreas, while pelvic scans are more about reproductive organs and surrounding tissues. The overlap part was useful too I didn’t know both could look at the bladder. I also appreciate the FAQ section; it clearly explains when a doctor might recommend each type of scan. This makes me feel more informed for my upcoming check-up, and I can ask smarter questions about which scan I might need.
This is so helpful! I always mixed these two up. Quick question though: If a doctor suspects something like appendicitis, which scan is usually the first one they order?
This was really informative, but it also made me a little uneasy 😟 If both scans can look at the bladder, how often do doctors miss something by choosing only one type of scan? For example, if someone has abdominal pain but the issue is actually related to reproductive organs, could an abdominal scan delay diagnosis? 🤔 I feel like patients aren’t always told why one scan is chosen over the other, and that lack of explanation can be stressful. Is it common practice to combine abdominal and pelvic scans, or does it depend heavily on symptoms and age?
This article made the differences between abdominal and pelvic scans really easy to understand! I didn’t realize how much overlap there can be, like checking the bladder in both types of scans. I always thought they were completely separate. Knowing that a pelvic scan can help monitor pregnancy and reproductive health in women, and prostate issues in men, is really useful. I also like the tip about combined scans makes sense if a full view of both areas is needed. I feel more confident now about discussing the right scan with my doctor if I ever have abdominal or pelvic concerns.
This was a really clear and helpful explanation. I never fully understood the difference between abdominal and pelvic scans before, but this broke it down perfectly. Thanks for sharing!